Describe Five Mechanisms Microorganisms Used to Develop Antimicrobial Resistance
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis most common mechanism Inhibition of Protein Synthesis Translation second largest class Alteration of Cell Membranes. All the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance can be narrowed into two part.
Define failure of drug therapy.
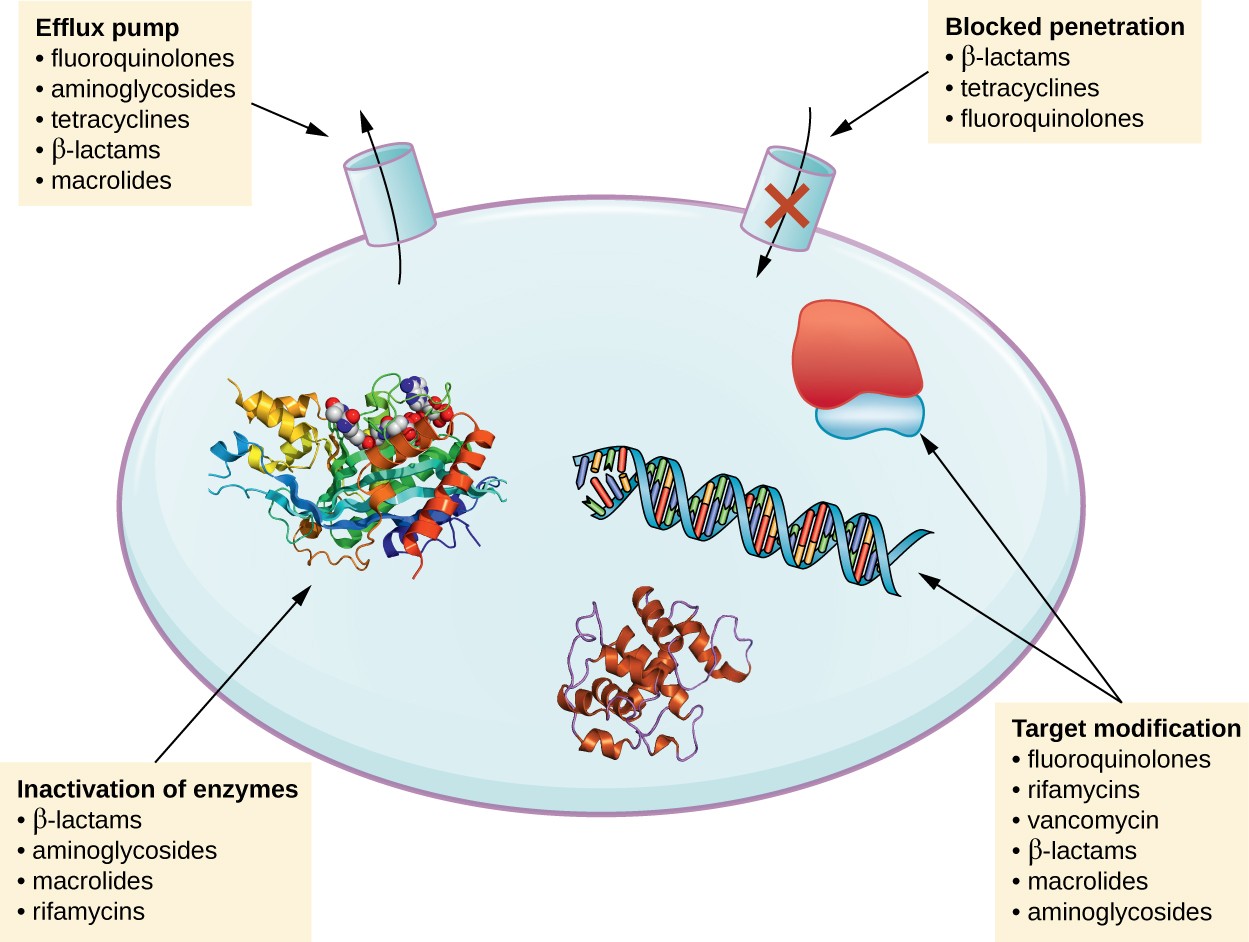
. Antibiotic resistance loss of susceptibility of bacteria to the killing bacteriocidal or growth-inhibiting bacteriostatic properties of an antibiotic agent. First the organism may acquire genes encoding enzymes such as -lactamases that destroy the antibacterial agent before it can have an effect. Second bacteria may acquire efflux pumps that extrude the antibac-.
Some make people crops or. How Antibiotic Resistance Spreads 1 Germs bacteria and fungi are everywhere. When a resistant strain of bacteria is the dominant strain in an infection the infection may be untreatable and life-threatening.
Mutation and horizontal gene transfer. In nature microbes are constantly evolving in order to overcome the antimicrobial compounds produced by other microorganisms. The five main mechanisms by which bacteria exhibit resistance to antibiotics are.
Antibiotics kill germs that cause infections. Ways that bacteria acquire resistance. Mechanisms of Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents Page 1 of 2 Abstract During the past decades resistance to virtually all antimicrobial agents has.
Human development of antimicrobial. Several mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance are readily spread to a variety of bacterial genera. The treatment of bacterial infections is increasingly complicated by the ability of bacteria to develop resistance to antimicrobial agents.
Gram-negative bacteria have an outer layer membrane that protects them from their environment. For example enzymatic deactivation of penicillin G in some penicillin-resistant bacteria through the production of β-lactamases. Selective pressure of use of that agent.
Examples of bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics include methicillin-resistant. But antibiotic-resistant germs find ways to survive. An important quality for an antimicrobial drug is selective toxicity meaning that it selectively kills or inhibits the growth of microbial targets while causing minimal or no harm to the host.
List current drug therapies used for treating such pathogenic resistant organisms. These pathogens develop resistance to carbapenems through a variety of mechanisms including production of carbapenemases broad-spectrum β-lactamases that inactivate all β-lactams including carbapenems active efflux of carbapenems out of the cell andor prevention of carbapenem entry through porin channels. Explain why they continue to fail and include methods to reduce failure of such therapies.
A common mechanism that bacteria use to become resistant to antibiotics is by modifying the target of the antibiotic. To modify or bypass the target that the antibiotic acts on. WHO has declared that AMR is one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity.
Pump the antibiotic out from the bacterial cell. Five Basic Mechanisms of Antibiotic Action against Bacterial Cells. Describe how microorganisms develop or acquire drug resistance.
Over time bacteria have evolved many different antibiotic resistance strategies to accomplish this. As bacteria grow and replicate they copy their genetic material the genome. The three fundamental mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance are 1 enzymatic degradation of antibacterial drugs 2 alteration of bacterial proteins that are antimicrobial targets and 3 changes in membrane permeability to antibiotics.
Antimicrobial agents are often categorized according to their principal mechanism of action. Antimicrobial resistance is not a new phenomenon. Mutation Through the process of cell replication some bacteria develop mutations that makes them resistant to antibiotics.
Germs restrict access by changing the entryways or limiting the number of entryways. Some resistant germs can also give their resistance directly to other germs. Restrict access of the antibiotic.
Mechanisms include interference with cell wall synthesis eg beta-lactams and glycopeptide agents inhibition of protein synthesis macrolides and. Mechanisms include interference with cell wall synthesis eg beta-lactams and glycopeptide agents inhibition of protein synthesis macrolides and tetracyclines interference with nucleic acid synthesis fluoroquinolones and rifampin inhibition of a metabolic pathway trimetho. Antimicrobial agents are often categorized according to their principal mechanism of action.
It requires urgent multisectoral action in order to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals SDGs. Antibiotic-resistant germs can multiply. There are lots of mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
Resistance Mechanisms Defense Strategies Resistance Mechanisms Defense Strategies Description. Describe the mechanism of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Describe the mechanisms of action associated with drugs that inhibit cell wall biosynthesis protein synthesis membrane function nucleic acid synthesis and metabolic pathways.
Antibiotic resistance mechanisms 1. They can carry more than 1 antibiotic resistance gene replicate independently of the chromosome and transfer between multiple species. 21 rows Apparently most pathogenic microorganisms have the capability of developing resistance to at.
Resistance plasmid R factor are extrachromosomal circular double-stranded DNA. Antibiotic resistance can be either plasmid mediated or mai. These bacteria can use this.
In this context both type of antibiotic resistance mechanisms will be discussed. Stop the antibiotic from reaching its target. Once bacterial cells acquire resistance exposure to antibiotics kills off non-resistance bacteria while the antibiotic-resistant bacteria proliferate.
Describe the different mechanisms of antimicrobial drug resistance. Mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antibiotics. Antimicrobial resistance AMR is a global health and development threat.
The last mechanism belongs to horizontal gene transfer-mediated resistance and most of the other mechanisms of. When they do this occasionally mistakes in the DNA sequences get included eg. An A gets replaced with a C.
Modification of the antibiotic target site. The first mechanism of development of antibiotic resistance is through limited uptake of a drug into the bacterial cell. The limited uptake is facilitated cell membrane impermeability to the drug molecules in the process of countering entry of toxic substances into the bacterial cell.
Mechanisms of Drug Resistance. Misuse and overuse of antimicrobials are the main drivers in the development. Drug inactivation or modification.
Some organisms use this mechanism in conjunction with efflux pumps to make resistance even more effective.

Schematic Diagram Highlighting The Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms Download Scientific Diagram

Mechanisms Of Antibiotic Resistance There Are Three Main Ways By Which Download Scientific Diagram

0 Response to "Describe Five Mechanisms Microorganisms Used to Develop Antimicrobial Resistance"
Post a Comment